Simply: what is phishing?
Phishing is a scam technique through which cybercriminals impersonate trusted entities to steal your personal data.
In a time when this type of attack is increasingly frequent, each reckless click can expose you to significant risks, ranging from identity theft to substantial financial losses.
That’s why it’s crucial to understand the threat in order to know how to protect yourself.
Looking to guard against phishing attempts? You’ve been a victim of phishing and want to know what to do? Then this article is for you.
Debugbar will explain phishing in simple terms, and you will discover how these fraudsters operate. And, more importantly, you’ll learn how you can effectively arm yourself against their tricks.
What is phishing?
Phishing is one of the favorite techniques used by cybercriminals.
The principle is pretty simple: they pretend to be a trusted entity to extort your sensitive information. Emails that look just like your bank’s, SMS messages that seem to come from your internet provider…
The tricks are numerous and ever more sophisticated. And in the whirlwind of everyday life, it’s easy to fall into the trap.
So, to avoid being a victim of this kind of scam, the first thing to do is understand how it works.

How does phishing work?
Phishing is mainly based on the principle of social engineering, i.e., the psychological manipulation of individuals.
To put it simply, attackers try to deceive their targets by pretending to be legitimate people or organizations.
The main goal is to get you to reveal private information, such as your passwords, your social security data or credit card pin numbers.
To do this, phishers have a well-established strategy:
- They start by studying their targets: What are their interests? Which companies or organizations do they trust? In short, what is their weak point?
- Once this preparatory work is done, phishers launch their attack and send a message (email, SMS, or phone call) carefully designed to look like an official communication from a trusted organization (for example, your bank or internet provider).
- This message often contains a link to a fraudulent website that looks exactly like the official site. Here you’ll be asked to enter your personal information… and that’s where the trap closes shut. You’ve given them the information they were hoping for. They can then carry out all kinds of malicious operations: identity theft, fraud, etc.
And let’s face it, in an era where we are constantly bombarded with emails and other messages, it’s very easy to be deceived. Especially since phishing attempts can take several forms.
What are the main forms of phishing?
Phishing is a persistent and evolving threat, taking many forms.
Among the most frequent types of phishing, we notably find:
- Email phishing: The most widespread form of phishing. Attackers send emails that appear to come from a legitimate company or organization in an attempt to get users to provide personal data.
- Smishing and Vishing: These are forms of phishing that use SMS (Smishing) and Voice call (Vishing). They may present themselves as an emergency message requiring immediate action.
- Spear phishing: This method targets specific individuals instead of a broad audience. With spear phishing, hackers personalize their messages with the victim’s name, position, phone number, and other information in an attempt to increase the appearance of legitimacy.
- Whaling: Whaling is a specific form of spear phishing that targets high-ranking company executives. The objective is often to gain access to sensitive information or carry out illicit financial transfers.
- Pharming: In this attack, phishers redirect users from a legitimate site to a fraudulent one even if the user doesn’t click on a malicious link.
Each type of attack has its own characteristics, but all have the same goal: to deceive users to gain access to their sensitive information.
As you can see, there really are quite a few forms of existing phishing and new ones will probably appear with the emergence of AI.
Fortunately (if we can say so), all these attacks have common criteria that can help us identify them. Let’s see what they are.

How to identify a phishing attack?
Identifying a phishing attempt can be really tricky, especially when phishers use sophisticated methods.
However, most phishing attempts use the same tricks. Some signs may therefore put you on alert. So you need to be particularly careful in spotting them.
So, be particularly wary when you receive a message with:
- An alarming tone: Phishing emails or SMS messages often try to create a sense of urgency. For example, they may tell you that your account will be closed unless you take immediate action.
- Haphazard spelling and grammar: Although many attackers now use high-quality translations, some messages may still contain quite coarse spelling or grammar mistakes.
- Solicitations for personal information: A legitimate company or organization will never ask you by email to provide them with your sensitive info (credit card pin, social security data, password, etc).
- Strange links: If you hover your mouse over a link in a suspicious message, your web browser should display the URL where the link will take you. If the URL looks strange, do not access it.
For example: if you receive a message from your bank and when hovering your mouse over the link you see a weird domain name such as acsfushvini-11453.com instead of www.yourbank.com, the email is likely to be a phishing attempt.
- A weird email address or phone number: Hackers usually use email addresses or phone numbers that have nothing to do with those of the organizations they are trying to imitate.
For example: if you receive an email from your internet service provider with one or more clickable links in the content. Always verify the sender’s email address before clicking on anything.
Click on the sender’s name at the top of the email and look at the address that appears. If it has nothing to do with your provider’s, close the email, block the sender and place it in your junk mail.
Remember, if you have suspicions about the nature of a received message, you can always directly contact the entity or company in question by another means to verify the validity of the message.
What does a phishing attempt look like: some examples
It’s easier to spot phishing attempts if you know what they look like. Here are a few examples:
- Emails from “your bank”: You receive an email pretending to be from your banker, asking you to confirm your banking details or reset your password. The provided links then direct you to a website that looks exactly like your bank’s, but in reality, it’s a trap to obtain your login details.
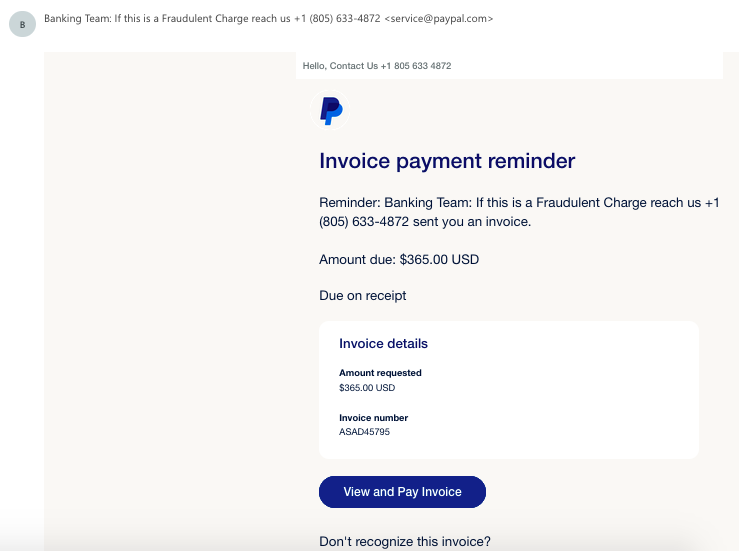
- Identity theft warnings: An email claims that your account has been compromised and that you need to verify your information to protect it. It could be an email account, a social network, or an account in an online store. Again, the provided link leads to a fake site intended to collect your information.

- Parcel waiting alert: You receive a text message or email informing you that a parcel is waiting and providing you with a link to arrange delivery or pay a missing amount. The link leads to a fake delivery website asking you to pay a small sum to rearrange delivery.
These examples clearly illustrate how phishers use sophisticated methods to deceive their victims and obtain their personal information.
Well, with all this, you should identify phishing attempts. But, even while being attentive, certain emails or messages can fool us. That’s why it’s important to remain extremely vigilant and adopt good practices to guard against attacks.
How to protect yourself from phishing attacks?
Protecting yourself from phishing requires a combination of technical measures and good personal practices.
- Adopt good personal practices
- Implement technical protection (anti-virus, anti-spam…)
- Train your team (for businesses)
- Keep your equipment up-to-date
Always check everything and be cautious
The best way not to get fooled is to be vigilant towards all the messages you receive. So:
- Try to see if there are grammatical errors, an urgent tone, or requests for personal information.
- Never share your passwords or sensitive information.
- Never click on links in an unsolicited email or text message. If you receive an email from your bank or another company with which you have an account, always visit their website by typing the URL into your browser rather than clicking on the link in the email.
- Always check the URL before clicking on a link to see where it actually leads.
- Always check the email address or number of the sender of the message.
- Use strong and unique passwords for each account. Don’t forget to change them regularly.

Implement a set of technical protections for your security
Preventing phishing attacks from reaching you is one of the best ways to protect yourself.
For this, there are several tools and techniques you can use for your security:
- Spam filters: Most modern email services offer some form of spam protection, which can filter out some spam and phishing attempts.
- Antivirus – anti-malware software: They can protect you by identifying and blocking phishing attempts, especially if they involve malware.
- Multi-factor Authentication (MFA): Always activate MFA for your important accounts. This means that a hacker needs to get more than just a password to access your account. It’s an extra lay of security.
Train your team
Working in a company? Well, bad news folks; you are among the hackers’ favorite targets. It is therefore crucial to protect yourself. And efficient protection primarily involves training your team regarding the digital dangers.
By making sure all your employees will adopt the right moves, you are already taking the first step towards a little more safety.
Perform updates and backups
Finally, it’s vital to keep your operating system, software, and applications up-to-date.
Updates often contain security fixes which help protect you against threats such as phishing and malware.
Moreover, regularly backup your important data. If you fall victim to a phishing spam, you can thus retrieve your data.
Unfortunately, if these measures arrive too late and you have been a victim of phishing, you need to act quickly to minimize the damage.
What to do when you’re the victim of a phishing attack?
If you fall prey to a phishing scam, it’s crucial to act quickly and:
- Change all your passwords: If you’ve clicked on a link and provided sensitive information, you should change your passwords immediately.
- Report the attack: Often, you have the chance to report directly from your email inbox or phone. You can also report it to the company that’s been impersonated. If you’ve been harmed or fear that the attack may cause damage or compromise your security, immediately report it and file a complaint with the police.
- Report the event to your bank: If you feel that your banking information has been compromised, contact your bank or the company you have your credit card with to report the problem and discuss the next steps.
- Have your device analyzed: Have your computer analyzed by an anti-malware or antivirus application to ensure no malicious software has been installed.
As unpleasant as a phishing attack may be, it’s important to remember that recovery is possible. By taking swift action and being prepared, you can minimize potential damages.

Phishing: what you need to remember
In conclusion, phishing is a technique used by cybercriminals to get hold of your sensitive information by impersonating a trusted entity. Phishing attacks are widespread and can be devastating, but by being well-informed and prepared, you can minimize your risk.
- Phishing is an ever-present threat, but recognizing common tactics used by phishers can help protect against them.
- There are several types of phishing attacks (spear phishing, whaling…).
- Adopting proven security measures, such as using strong passwords, regularly performing software updates, and adhering to strict email policies, can reduce your vulnerability to phishing attacks.
- If you fall victim to a phishing attack, act quickly by changing your passwords, reporting the incident to the relevant authorities, and closely monitoring your financial accounts.
The importance of reporting phishing attempts should not be underestimated. By reporting attacks, not only will you help prevent other victims but also provide valuable information to the authorities in combating these crimes.
Undeniably, phishing is a major threat in today’s cybersecurity landscape, and it requires constant vigilance and a deep understanding of the various tactics employed by criminals to effectively protect against these attacks.